
Nutrition is fundamental to health and well-being. It provides the body with the necessary energy, vitamins, and minerals required for growth, repair, and maintenance. Understanding the various types of nutrition is essential for making informed dietary choices. This article delves into the different types of nutrition, their importance, and how they impact overall health.
What is Nutrition?
Nutrition is the process by which living organisms obtain and utilize food to support their life functions. It involves the intake, absorption, and assimilation of nutrients, which are substances that provide the body with essential elements needed for energy, growth, and maintenance.
The Six Essential Nutrients
Before exploring the types of nutrition, it’s important to understand the six essential nutrients that the body needs:
Carbohydrates: It gives energy for our daily lives.
Proteins: Necessary for growth, repair, and maintenance of tissues.
Fats: Supply energy, support cell growth, and protect organs.
Vitamins: Required for various biochemical processes in the body.
Minerals: Important for bone health, fluid balance, and other bodily functions.
Water: Crucial for maintaining hydration, temperature regulation, and various metabolic processes.
Types of Nutrition
Nutrition can be broadly categorized into several types based on dietary habits and nutritional needs. Here are the primary types of nutrition:
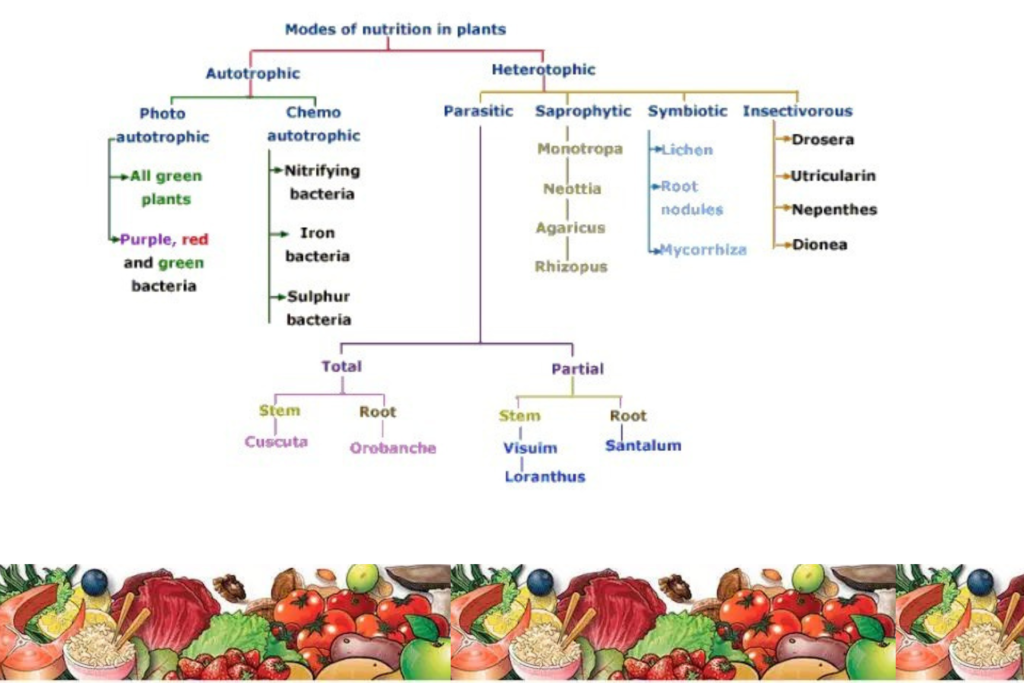
1. Autotrophic Nutrition
Autotrophic nutrition is the mode of nutrition in which organisms synthesize their own food from simple substances like carbon dioxide and water. This process typically involves photosynthesis, where light energy is converted into chemical energy.
Key Points:
Involves photosynthesis.
Primarily seen in plants and algae.
Produces oxygen as a byproduct.
2. Heterotrophic Nutrition
Heterotrophic nutrition involves organisms obtaining their food from other organisms. Animals, fungi, and most bacteria are heterotrophs. This type of nutrition can be further divided into subtypes:
a. Herbivorous Nutrition
Herbivores are animals that consume plant material. Their diet consists of leaves, fruits, seeds, and other plant parts. Examples include cows, deer, and rabbits.
b. Carnivorous Nutrition
Carnivores are animals that eat other animals. Their diet includes meat from prey animals. Examples include lions, tigers, and wolves.
c. Omnivorous Nutrition
Omnivores consume both plant and animal matter.
d. Saprophytic Nutrition
Saprophytes obtain nutrients from decaying organic matter. Fungi and certain bacteria are saprophytes. They play a critical role in decomposition and nutrient cycling in ecosystems.
e. Parasitic Nutrition
Parasites derive nutrition from living hosts, often harming them in the process. Examples include tapeworms, fleas, and some bacteria.
3. Mixotrophic Nutrition
Mixotrophic nutrition involves organisms that can switch between autotrophic and heterotrophic modes of nutrition depending on environmental conditions. Some protists and algae exhibit mixotrophic behavior.
Key Points:
Can synthesize their own food or obtain it from other organisms.
Adaptable to varying environmental conditions.
4. Holistic Nutrition
Holistic nutrition focuses on the idea that food should be viewed as a whole, emphasizing the interconnectedness of diet, health, and overall well-being. It promotes a balanced diet rich in whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, while minimizing processed foods and artificial additives.
Key Points:
Emphasizes whole, natural foods.
Integrates physical, mental, and emotional health.
Encourages mindful eating practices.
5. Medical Nutrition Therapy (MNT)
Medical Nutrition Therapy involves the use of specific nutritional interventions to manage medical conditions and improve health outcomes. It is often prescribed by healthcare professionals and tailored to individual needs. Conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and gastrointestinal disorders can benefit from MNT.
Key Points:
Customized to individual health conditions.
Aims to manage and improve specific medical issues.
Often involves a registered dietitian or nutritionist.
6. Sports Nutrition
Sports nutrition is designed to optimize athletic performance and recovery through dietary strategies. It focuses on the right balance of nutrients to support training, enhance endurance, and promote muscle repair and growth. This type of nutrition often includes supplements like protein powders, electrolytes, and energy bars.
Key Points:
Tailored to athletes and active individuals.
Enhances performance and recovery.
Involves strategic nutrient timing and supplementation.
7. Functional Nutrition
Functional nutrition considers the individual as a whole and how diet impacts overall health. It aims to identify the root causes of health issues and address them through personalized nutrition plans. This approach often involves comprehensive assessments and targeted dietary changes.
Key Points:
Personalized to the individual’s unique needs.
Addresses underlying causes of health problems.
Integrates diet with other lifestyle factors.
8. Sustainable Nutrition
Sustainable nutrition emphasizes dietary choices that are not only healthy but also environmentally sustainable. It advocates for consuming more plant-based foods, reducing food waste, and choosing locally sourced, organic products. This type of nutrition aims to support both human health and the health of the planet.
Key Points:
Promotes environmentally friendly eating habits.
Encourages plant-based diets.
Aims to reduce the carbon footprint of food production.

The Importance of Balanced Nutrition
Balanced nutrition is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. Here’s why it matters:
Supports Growth and Development
It ensures that they receive the necessary nutrients for proper physical and cognitive development.
Maintains Energy Levels
A balanced diet provides the energy needed for daily activities and physical performance. Carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are key energy sources.
Boosts Immune Function
Essential nutrients, such as vitamins and minerals, play a vital role in supporting the immune system.
Promotes Healthy Weight
Balanced nutrition helps in maintaining a healthy weight by providing the right mix of nutrients without excessive calories.
Enhances Mental Health
Certain nutrients, such as omega-3 fatty acids, B vitamins, and antioxidants, are linked to improved mental health and cognitive function. Proper nutrition can help manage stress, anxiety, and depression.
Reduces Risk of Chronic Diseases
It helps in managing blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and blood sugar levels.

Tips for Achieving Balanced Nutrition
Achieving balanced nutrition involves making informed dietary choices. Here are some tips to help you maintain a balanced diet:
Include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, proteins, and healthy fats in your diet.Be mindful of portion sizes to avoid overeating. Limit Processed Foods.Minimize the intake of processed and junk foods high in sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats. Opt for whole, unprocessed foods whenever possible.Meal prepping can help you stick to a balanced diet.Everyone’s nutritional needs are unique, so adjust your diet based on what works best for you.
Understanding the different types of nutrition is essential for making informed dietary choices that support overall health and well-being. Whether it’s adopting a holistic approach, tailoring your diet to specific health conditions, or focusing on sustainability, each type of nutrition offers unique benefits. By embracing balanced nutrition and mindful eating practices, you can enhance your health, boost your energy levels, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Unlock the power of nutrition and embark on a journey towards a healthier, more vibrant life.



